This article sets out some key basic information for running an ARK: Survival Evolved server on AMP.
1. Dependencies on Windows
ASE requires the following dependencies on Windows:
-
DirectX End-User Runtimes (June 2010) (if the web installer doesn’t work, you can download the files from here and manually install them)
You will also need X86 Visual C++ Redistributable Packages for Visual Studio 2015-2022 to run SteamCMD in AMP to install the server.
2. Ports
ASE uses three key ports:
- Game Port: 7777 UDP by default
- Peer Port: 7778 UDP by default (you might see this called Reserved Port in AMP if you have an older instance)
- Query Port: 27015 UDP by default
All three ports need to be port forwarded (if you’re on a NAT network). Check what ports are actually allocated to your instance by clicking on the “Edit Ports” button for the instance.
The query port is used for finding and connecting to the server in Steam. The game port is used for finding and connecting to the server in-game. The peer port is used by the Steam P2P protocol for in-game browser advertising.
The template also configures an RCON Port: 27020 TCP by default. You can use this port to connect to the server’s RCON by an external RCON client if needed.
The server always opens the Peer Port on Game Port + 1 - so make sure the ports allocated in AMP are also sequential for those ports.
3. Settings
NOTE: There are three templates available in AMP for ASE. Two of them use a “minimal” template that has far fewer settings in the AMP UI - basically those that can only be configured by command line arguments, plus a few other key settings for the player limit, mods and RCON. These templates are designed for those users who prefer to use a tool like Beacon to configure GameUserSettings.ini and Game.ini for their server, with one of the templates also being configured to install the Ark Server API.
The other template has many more (but not all) settings in the UI. The discussion below primarily applies to that template.
Almost all settings that can be configured on the command line or in GameUserSettings.ini and that are listed here are included in AMP’s UI.
A number of settings that can be configured in Game.ini are also included.
You can search for a setting using its formal name (eg AutoDestroyStructures) using AMP’s search bar to find it in AMP’s UI.
If there is a particular setting that is not included in AMP’s settings, you can either add it as a command line flag or option (as appropriate) or add it directly to GameUserSettings.ini or Game.ini, as needed. Take care not to repeat a setting that is already in AMP’s UI!
Configuration files are located in ShooterGame/Saved/Config/LinuxServer or ShooterGame\Saved\Config\WindowsServer as applicable.
Warning: The ASE server can overwrite and/or reset GameUserSettings.ini in particular if it is missing key components or has incorrect data. Be careful when editing the config files manually. Otherwise, you may find that some of the settings in AMP’s UI no longer continue to work.
4. Mods
4.1 Installing/updating
4.1.1 Automatic method
Usually the easiest way to manage mods on the server is to let either AMP or ASE manage them. One of these two options can be selected under “Mod Management Mode”:
- AMP manages: When the server is updated, AMP will run a script that uses SteamCMD to download the mods, with retries if needed, such as for larger mods. It will then install the mods in the
ShooterGame/Content/Modsdirectory, and create the associated.modfiles. - ARK manages: When the server is started, ASE will run SteamCMD to download the mods, and then try to install them in the required directory and create the
.modfiles.
Especially on Windows, ASE’s system can sometimes fail to download particularly large mods, given it doesn’t retry if SteamCMD times out. Also, even if a mod is fully downloaded, on Windows ASE can sometimes fail to install them in the required directory if the system paths that the mod files are downloaded to are too long. Either way, the mod will not be functional, either partially or fully.
AMP’s script doesn’t have these issues. It may however be slower than ASE’s system. Note that the script does require some dependencies, which it will either manage or prompt you to install.
If either the AMP or ASE automatic method is enabled, it will manage the mods listed in “Mods List” (as a comma-separated list of IDs, like 1984936918,1785880078).
Make sure your mods list is just one line - no line breaks or carriage returns.
Note that if you are using the Server API version of the ASE template (see section 8), the ASE system will not work on Linux. You will need to use the AMP method if you want mods automatically handled.
4.1.2 Manual method
If preferred, mods can be manually added to the ShooterGame/Content/Mods directory.
Add the mods to your client, start it, and then copy over the mod directory and .mod file that is generated to your server. Use AMP’s SFTP to copy the files to ensure file permissions are correct on the server.
The manual method could be useful if you want to use specific versions of mods.
4.2 Loading
Any non-map mods that are listed in “Mods List” will be loaded by the server when started, as long as the associated mod files are in ShooterGame/Content/Mods (either by automatic download or manually).
Map mods can’t be loaded this way. The name of the map needs to be specified under “Custom Map Name”, and the Custom map type selected under “Map".
However, map mods can still be listed (by ID) in “Mods List” if you want them automatically downloaded/updated by “Mod Management Mode”.
5. Server binding
By default the ASE server is bound to the application IP binding set for the instance. This is normally 0.0.0.0 (all interfaces) unless it has been changed under New Instance Defaults.
If you have multiple IPs on your host, you may wish to bind the server to one of them. You can do this by changing the Application IP Binding for the instance.
The IP binding set in this way must be one that AMP itself can reach. Otherwise AMP will not be able to connect to ASE’s RCON, and therefore won’t detect when the server is started. As well, logging output to the console, and input from the console, will not be enabled. This can particularly be an issue if the server is bound to a public IP (such as on a VPS). Generally it is better to keep the binding as 0.0.0.0.
6. Clusters
Options for clusters are included in the ARK SE Clusters menu.
The key options are “Cluster Directory Override” and “Cluster ID”. Each ASE instance using the cluster must have access to the cluster directory, and must have the same cluster ID specified. “Enable Cluster” must also be set.
Platform-specific instructions for the cluster directory are set out below.
The cluster ID can be any string of numbers and letters, such as cluster1 or 85467fhsjcfk.
6.1 Windows
You can place the cluster directory wherever you like on your system, as long as the NETWORK SERVICE user owns the directory and has access to the path.
For example, you could create:
\AMPDatastore\arkcluster
Right click on the directory in Windows Explorer (noting that you should generally not use Windows Explorer for AMP’s files, to avoid breaking file permissions), and set the ownership under Properties>Security.
The “Cluster Directory Override” in each ASE instance would then be specified as \AMPDatastore\arkcluster.
You may also need to specify the relevant drive letter (such as C:) if you have multiple drives on your system.
6.2 Linux
You can place the cluster directory wherever you like on your system, as long as the amp user and group owns the directory and has access to the path.
Additional steps are required for any ASE instances in Docker.
6.2.1 Instances not in Docker
For example, you could create:
/home/amp/arkcluster
Make sure the amp user and group owns this directory by running as root:
chown -R amp:amp /home/amp/arkcluster
6.2.2 Instances in Docker
Follow the steps in section 6.2.1 to set up the cluster directory on the system.
Then you have to do some more configuration to ensure the cluster directory is mounted in the Docker containers.
This involves specifying CustomMountBinds for each ASA instance in instances.json.
For AMP version 2.6.10+, the easiest way to do this is to click on the “pencil” icon on the instance, and navigate to the Storage tab. For prior AMP versions, it must be done manually in the file, which is usually in /home/amp/.ampdata/ (and both ADS and the relevant instances need to be restarted for this to take effect - restart ADS first).
Examples are below. In these examples, it is assumed that the cluster directory is created on the host system in /home/amp/arkcluster.
-
For ASE instances that are not using the minimal template:
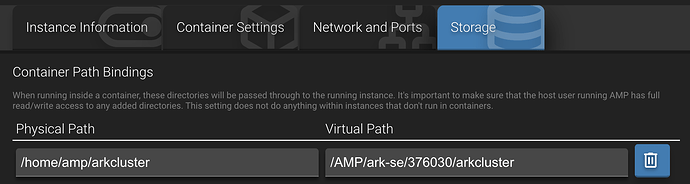
When using the AMP UI:
When editing
instances.jsondirectly:"CustomMountBinds": {"/home/amp/arkcluster":"/AMP/ark-se/376030/arkcluster"},The “Cluster Directory Override” in each ASA instance would then be specified as
/AMP/ark-se/376030/arkcluster. -
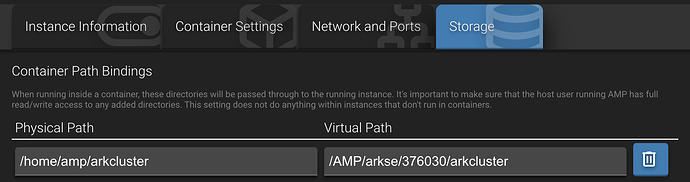
For ASE instances that are using the minimal template:
When using the AMP UI:
When editing
instances.jsondirectly:"CustomMountBinds": {"/home/amp/arkcluster":"/AMP/arkse/376030/arkcluster"},The “Cluster Directory Override” in each ASA instance would then be specified as
/AMP/arkse/376030/arkcluster.
The above are only examples. However, mounting the cluster directory in the way suggested has the benefit that it will then be visible in the AMP File Manager for each instance.
7. Backup exclusions
The template is configured to download two default backup exclusion files, which result in AMP’s backups of the ASE instance excluding most of the server content (anything that is not specific to the server and can simply be downloaded via SteamCMD again).
The relevant .backupExclude files are installed in the server base directory, and in the ShooterGame subdirectory.
You can modify these .backupExclude files to add or remove exclusions as desired. Or you can delete them entirely and disable the default file download under the Updates menu.
8. Server API
One of the templates is configured to install the Ark Server API. This allows plugins to be run on the server.
To enable the Server API to run on Linux, the template uses Wine to run the server.